
Why UWB is a Great Enhancement to Secured Payments
In the rapidly evolving landscape of contactless payments, two technologies have garnered significant attention: Near Field Communication (NFC) and ultra-wideband (UWB).
While NFC has been the cornerstone of contactless transactions for years evolving from card-based technology towards the use in manifold electronic devices such as smartphones and Wearables, UWB is emerging as a great enhancement for the ecosystem, offering a better user experience, convenience, and security. This article explores why UWB will play a major role in the future of secured contactless payments.
Understanding NFC and UWB Payments
NFC is a short-range wireless communication technology operating at 13.56 MHz, enabling secure authentication and data exchange between cards, readers, and mobile devices within a few centimeters. It's widely used in contactless payment systems, access control, Transport, ID documents, and data sharing. The technology's simplicity, the standardized ease of use, as well as the certifiable security level, have contributed to its widespread adoption.
UWB, on the other hand, is a time-of-flight and impulse-based radio technology, using wide channels of about 500MHz in a broad frequency spectrum (3.1 to 10.6 GHz) to precisely measure positions or transmit data over short distances. Originally developed for radar applications, UWB has found its way into consumer electronics with capabilities like precise location tracking even in harsh or indoor locations and, if properly implemented, secure data transmission.
Comparing NFC and UWB Payments
Payment Security Considerations
Security is paramount in contactless payments. NFC transactions are generally secure but only work at small distances up to 10 cm. Alternative technologies offering a longer range such as Bluetooth® Low Energy or Wi-Fi are susceptible to relay attacks, where an attacker intercepts and relays communication between the card and terminal, potentially leading to unauthorized transactions or authentications.
Since convenience must not be traded against security, UWB standards have been designed to address these security concerns through its precise distance measurement capabilities, features such as Scrambled Time Sequences (STS), and dedicated keys generated and monitored by hardware-based secure elements.
UWB can therefore accurately and securely determine the distance before any action is taken, making it difficult for attackers to execute relay attacks. The FiRa® Consortium highlights UWB's ability to provide precise, secured, and reliable distance measurements making it an ideal wireless solution for modern security challenges. Additionally, the Security Working Group within FiRa is constantly working jointly within the UWB ecosystem to define the right security measures against potential attacks and use case-specific security implementations.
Payment User Experience and Convenience
NFC requires users to bring their devices within a few centimeters of the payment terminal, which still necessitates a deliberate action. However, in car-related use cases such as toll collection or car parks, this can be secure yet inconvenient. UWB enhances the user experience by enabling hands-free, touchless payments. For instance, with UWB, a user could make a payment by simply walking past a terminal, with the transaction authenticated based on proximity and movement direction. This seamless interaction reduces friction and can provide the same level of security. UWB typically works hand-in-hand with other technologies in smartphones or wearables such as BLE for wake-up and data transmission and NFC for initial pairing and as backup in legacy infrastructures.
UWB Industry Contactless Payment Adoption and Future Prospects
The industry has started to recognize UWB's potential in secure contactless payments. Since 2019, many companies released secure UWB chips to enhance hands-free access control and payments used in several mobile phone and wearable platforms. Approximately 1.5 billion devices have been shipped through 2023 according to ABI.
Additionally, financial institutions are exploring UWB for peer-to-peer payments. For example, in 2022, ING Bank piloted a UWB-based payment solution that allows users to transfer funds by simply pointing their phones at each other, eliminating the need to exchange personal information.
In 2023, FiRa released a white paper about how UWB can revolutionize the public transport use case, and in 2024 FiRa published a leaflet, Tap-free Mobile Payments. Also in 2024, JCB and Sony showed a demo during the FiRa Osaka Face-to-Face Plenary Meeting showcasing the convenience of UWB-supported payments.
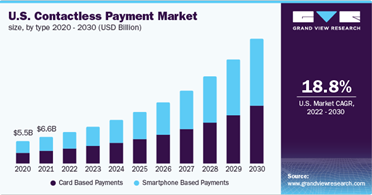
According to Grand View Research, the global contactless payment market was valued at approximately 34.55 billion USD in 2021 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.1% from 2022 to 2030. The demand for secure and convenient payment methods is behind this growth. Also, UWB's superior security features and user-friendly experience position it well to capture a significant share of this growing market.
Touchless Payments: Looking Ahead
While NFC has served as a reliable technology for contactless payments, authentication, and transport and will continue to do so in many applications, UWB offers compelling enhancements in convenience and user experience.
Its ability to enable seamless, hands-free transactions greatly enhances user convenience. As the industry continues to prioritize both security and user experience, UWB is well-positioned to become a significant asset in the future of secure touchless payments. With ongoing technological advancements, broader integration of UWB in smartphones, and growing consumer demand, we anticipate even wider adoption of UWB across applications beyond payments—such as secure access and personalized retail experiences—further revolutionizing how we interact with technology in our daily lives.